Technology acceptance model

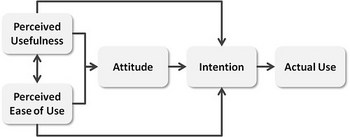
The technology acceptance model is an information systems theory that models how users come to accept and use a technology. The actual system use is the end-point where people use the technology. Behavioral intention is a factor that leads people to use the technology. The behavioral intention is influenced by the attitude which is the general impression of the technology. The model suggests that when users are presented with a new technology, a number of factors influence their decision about how and when they will use it, notably: • Perceived usefulness – This was defined by Fred Davis as "the degree to which a person believes that using a particular system would enhance their job performance". It means whether or not someone perceives that technology to be useful for what they want to do. • Perceived ease-of-use – Davis defined this as "the degree to which a person believes that using a particular system would be free from effort".
Get all relevant videos
Diffusion (business) - In business, diffusion is the process by which a new idea or new product is accepted by the market. The rate of diffusion is the speed with which the new idea spreads from one consumer to the next.
Diffusion of innovations - Diffusion of innovations is a theory that seeks to explain how, why, and at what rate new ideas and technology spread. The theory was popularized by Everett Rogers in his book Diffusion of Innovations, first published in 1962.
Domestication theory - Domestication theory is an approach in Science and Technology Studies and media studies that describe the processes by which technology is 'tamed' or appropriated by its users.
Lazy user model - The lazy user model of solution selection is a model in information systems proposed by Tétard and Collan that tries to explain how an individual selects a solution to fulfill a need from a set of possible solution alternatives.
New product development - In business and engineering, product development or new product development covers the complete process of bringing a new product to market, renewing an existing product and introducing a product in a new market. A central aspect of NPD is product design, along with various business considerations.
Product life cycle management - Product life-cycle management is the succession of strategies by business management as a product goes through its life-cycle. The conditions in which a product is sold changes over time and must be managed as it moves through its succession of stages.
Innovation economics
Sociology of culture
Diffusion
Product development
Product lifecycle management
Technological change
Science and technology studies
Product management
Technology in society
You may also interested in...
Total Images: 870